Orchestrate
.procfwk
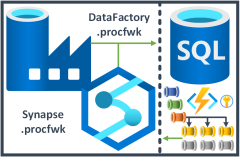
A cross tenant metadata driven processing framework for Azure Data Factory and Azure Synapse Analytics achieved by coupling orchestration pipelines with a SQL database and a set of Azure Functions.
- Overview
- Contents
Deploying ProcFwk
ProcFwk Deployment Steps
Below are the basic steps you’ll need to take to deploy the processing framework to your environment. Currently these steps assume a new deployment is being done, rather than an upgrade from a previous version of the framework. In addition, a reasonable working knowledge of using the Microsoft Azure platform is assumed when completing these action points.
Please see Service Tiers for details on the recommended minimum levels of compute to deploy.
Note; in the case of most deployment steps, things can be tailored to your specific environment requirements. For example:
- Using an existing SQL database or Key Vault.
- Creating granular function level permission keys.
- Using managed identity’s to authenticate between your functions and pipelines.
These custom setups are valid and given your knowledge of Azure can easily be applied. Otherwise the below steps offer a minimum vial product set of configurations.
Azure Resources
- Deploy an orchestration resource, either an Azure Data Factory instance or an Azure Synapse Analytics instance and connect it to source control - recommended, but not essential.
- Grant the respective orchestrators MSI access to itself as an owner to support the framework utilties pipeline already running checks.
- Create a SQL database using your preferred hosting environment.
- Create an Azure Functions App, a Consumption App Service Plan is fine for the processing framework, see service tiers for more details.
- Optionally create an Azure Key Vault resource.
- Used to store your orchestrators Linked Service connection credentials.
- Used to house SPN details when authenticating against worker pipelines.
Key Vault Secrets
If using Azure Key Vault, complete the following steps, otherwise jump to the next section.
- Grant your orchestrator access to Key Vault with it’s MSI using a Key Vault Access Policy.
- Add the Function App default key to Key Vault as a secret.
- Add a SQLDB connection string to Key Vault as a secret using your preferred authentication method.
- For SQL Authentication, add user details to the connection string.
- For an MSI, in the database grant Data Factory access using the following example code snippet.
CREATE USER [##Data Factory Name##] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER;
Deploying Code
- Publish the SQLDB project (MetadataDB) from Visual Studio or your preferred tool. From Visual Studio this will involve creating a new publish profile if you don’t have one already to your target database and instance.
- As part of the development of the processing framework a set of default metadata is included in the database project. If you don’t want these example values execute the following stored procedure to clear all data from the database.
EXEC [procfwkTesting].[CleanUpMetadata];
- As part of the development of the processing framework a set of default metadata is included in the database project. If you don’t want these example values execute the following stored procedure to clear all data from the database.
- Publish the Function App from Visual Studio or your preferred tool. From Visual Studio create a publishing profile or download a profile from the Azure Portal Functions App overview page.
Service Principals
- Optionally create a Service Principal to be used when deploying your orchestrator to your Azure Tenant.
- Create a Service Principal for the your orchestrator to authenticate and execute your worker pipelines.
- Grant the Service Principal Owner access to the target orchestrator containing your worker pipelines.
If Using Azure Data Factory
- Optionally deploy the procfwk pipelines and components using the PowerShell script DeployProcFwkComponents.ps1 and providing authentication details (via an SPN or using your own AAD account as a one off with the cmdlet Connect-AzAccount). For more details on using this PowerShell module to deploy Data Factory, see PoSH Deployment of ADF Parts.
- Optionally, if using a Git connected Data Factory instance its also possible to simply copy components from the processing framework repository into your target repository.
If Using Azure Synapse Analytics
- Copy the JSON resource definition files for all parts of the processing framework (dataset, linked services, pipelines) from the procfwk GitHub repository into the repository connected to your Synapse instance.
Checking Your Orchestrator
- Refresh your orchestrator via the developer UI to review the components deployed.
- Test all Linked Services connections (Key Vault, Functions and SQLDB) and update credentials as required for your environment connections.
- Publish the Data Factory via the developer UI if it hasn’t been deployed already.
Adding Metadata
- Add a set of default properties to the database its been cleared using the following stored procedure:
EXEC [procfwkHelpers].[SetDefaultProperties]; - Add at least one Tenant ID to the metadata database table.
- Add at least one Subscription ID to the metadata database table and connected to the correct Tenant ID.
- Add a target orchestrator where your worker pipelines exist, this can be the same orchestrator instance as the framework pipelines. Ensure the orchestrator is connected to the correct Subscription ID.
- Add your worker pipeline(s) and execution stage(s) metadata as required. See how to pre-populate metadata from an existing Data Factory if required.
- Set the attribute IsFrameworkOrchestrator within the Orchestrators table to identify which orchestrator resource will house and handle the framework pipelines.
- Set the database property ‘SPNHandlingMethod’ to your preferred method of handling. Via the metadata database directly or using Azure Key Vault, see SPN Handling for more details.
- Add your SPN details used to execute worker pipelines to your metadata. Use the following example code snippet.
EXEC [procfwkHelpers].[AddServicePrincipalWrapper] @DataFactory = N'FrameworkFactory', @PrincipalIdValue = '$(CLIENT_ID)', @PrincipalSecretValue = '$(CLIENT_SECRET)', @PrincipalName = '$(CLIENT_NAME)'; - Add any worker pipeline parameters as required.
- Optionally add recipients for email alerting. Use the following example code snippet. See email alerting for more details on this feature.
INSERT INTO [Recipients]
(
[Name],
[EmailAddress],
[MessagePreference],
[Enabled]
)
VALUES
(
'Alerting User 1',
'autoalerts@procfwk.com',
'TO',
1
);
EXEC [procfwkHelpers].[AddRecipientPipelineAlerts]
@RecipientName = N'Alerting User 1',
@PipelineName = 'Worker Pipeline 1',
@AlertForStatus = 'Success, Failed';
- Set the database property ‘FailureHandling’ to your preferred method of handling. See Fail Handling for more details on this feature.
- Optionally, perform a manual execution of the stored procedure ‘MetadataIntegrityChecks’.
EXEC [procfwk].[CheckMetadataIntegrity]
@DebugMode = 1;
Execute
- Debug or trigger the parent pipeline :-)
For more support deploying the processing framework see the video guide playlist on YouTube: